The Impact of Nuclear Power Plant on Life
The Impact of Nuclear Power Plant on Life
The event will be: “Live” in presence (if allowed by the covid rules, otherwise it will be online)
Short presentation of the event: Since climate change is, in the long run, the greatest threat to the survival of humanity and life in general, in recent years there have been intense debates about how good and how bad nuclear energy has brought us and what role it may play in the future. Through a short introductory interactive lecture, students will be introduced to examples of the impact of technology on the economy, environment and population. They will learn that every technological advancement has a specific impact on the environment, so the task of geography is to assess the risk and reduce the consequences of accidents in the form of a functional spatial organization. Do we consider nuclear power plants to be pure energy producers, can nuclear power plants explode like a nuclear bomb, is nuclear energy the last in terms of the number of lives lost per unit of energy produced, why do disagreements arise about the impact of nuclear power plants on the environment? waste you will learn in this interesting interactive lecture.
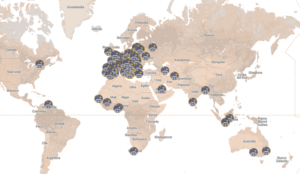
The Workshop: Students will use the link showing the spatial distribution of the largest nuclear accidents to identify the parts of the world affected by a nuclear accident. Using the attached material and ICT, they will investigate the three most famous nuclear accidents on a global scale: Chernobyl, Fukushima and the Kyshtym disaster. Electromagnetic pollution is any amount of radiation greater than natural. It is partly due to the radiation of the Sun and the Earth, but still, most of it comes from man-made sources. Students will be introduced to the division into ionized and non-ionized radiation as properties of each of the spectra. Through various demonstration experiments, they will learn about the propagation of energy using EM waves and will distinguish between harmful and harmless radiation.
Since climate change is, in the long run, the greatest threat to the survival of humanity and life in general, in recent years there have been intense debates about how good and how bad nuclear energy has brought us and what role it may play in the future. Through a short introductory interactive lecture, students will be introduced to examples of the impact of technology on the economy, environment and population. They will learn that every technological advancement has a specific impact on the environment, so the task of geography is to assess the risk and reduce the consequences of accidents in the form of a functional spatial organization. Do we consider nuclear power plants to be pure energy producers, can nuclear power plants explode like a nuclear bomb, is nuclear energy the last in terms of the number of lives lost per unit of energy produced, why do disagreements arise about the impact of nuclear power plants on the environment? waste you will learn in this interesting interactive lecture.
The Workshop: Students will use the link showing the spatial distribution of the largest nuclear accidents to identify the parts of the world affected by a nuclear accident. Using the attached material and ICT, they will investigate the three most famous nuclear accidents on a global scale: Chernobyl, Fukushima and the Kyshtym disaster. Electromagnetic pollution is any amount of radiation greater than natural. It is partly due to the radiation of the Sun and the Earth, but still, most of it comes from man-made sources. Students will be introduced to the division into ionized and non-ionized radiation as properties of each of the spectra. Through various demonstration experiments, they will learn about the propagation of energy using EM waves and will distinguish between harmful and harmless radiation.
Objectives: – investigates the positive and negative effects of nuclear technology on the population, the economy and the environment
– analyzes the consequences of nuclear accidents
– assumes the possible consequences of the failure of nuclear technology on the environment and spatial organization
– explains the problem of nuclear waste disposal on the example of NPP Krško
– the impact of electromagnetic radiation on the environment
– demonstrates the propagation of energy by electromagnetic waves (determination of wavelength)
– distinguishes between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation
Event language: Croatian (hrvatski)
Country: Croatia / Hrvatska
City: Zagreb
Reference person: Ružica Lončar, Geography teacher and Vanja Vučinić, Physics teacher
Role or Function: Geography teacher and Physics teacher
Reference Organization (if any):
Those who organize are: Academics
Expected duration: around 2 hours
Event program: place (the address) of the event is Klaićeva 7, Zagreb and the time of the event 13.00 h
ID.U.N.472